Rat TNF-α enzyme-linked immunoassay kit
| Specification | 96 Test |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.08 pg/ml (50 μl);0.16 pg/ml (10 μl) |
| Standard Curve Range | 1.37~1000 pg/ml |
| Standard Curve Gradient | 7 Points/3 Folds |
| Number of Incubations | 2 |
| Detectable sample | Liquid phase sample of soluble substances. For example: serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant, tissue grinding liquid, etc. |
| Sample Volume | 50 μl/10 μl |
| Type | Full-Ready-to-Use |
| Operation Duration | 120min |
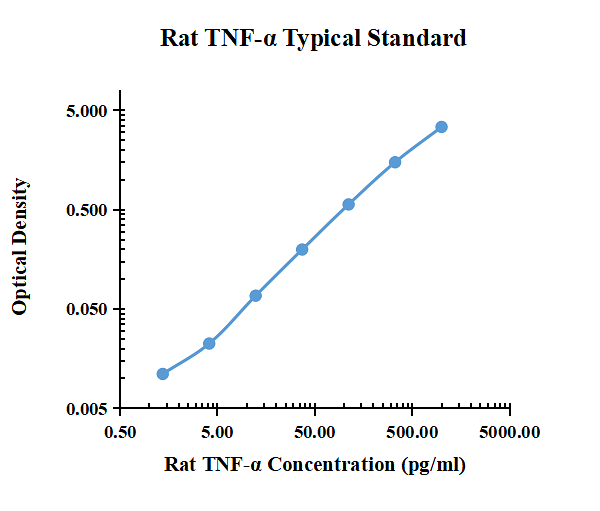
| pg/ml | O.D. | Average | Corrected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.0353 | 0.0308 | 0.0331 | |
| 1.37 | 0.0482 | 0.0401 | 0.0442 | 0.0111 |
| 4.12 | 0.0569 | 0.0541 | 0.0555 | 0.0225 |
| 12.35 | 0.1048 | 0.0974 | 0.1011 | 0.0681 |
| 37.04 | 0.2352 | 0.2276 | 0.2314 | 0.1984 |
| 111.11 | 0.6121 | 0.5822 | 0.5972 | 0.5641 |
| 333.33 | 1.568 | 1.495 | 1.5315 | 1.4985 |
| 1000.00 | 3.488 | 3.370 | 3.4290 | 3.3960 |
Precision
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample Number | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
| 22 | 22 | 22 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Average(pg/ml) | 23.2 | 99.7 | 315.4 | 21.5 | 96.1 | 288.4 |
| Standard Deviation | 1.3 | 4.3 | 12.8 | 6.9 | 3.1 | 1.0 |
| Coefficient of Variation(%) | 5.5 | 4.3 | 4.1 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 4.8 |
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay) Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays) Three samples of known concentration were tested six times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Spike Recovery
The spike recovery was evaluated by spiking 3 levels of human IL-6 into health rat serum sample. The un-spiked serum was used as blank in this experiment. The recovery ranged from 97% to 108% with an overall mean recovery of 103%.
Sample Values
| Sample Matrix | Sample Evaluated | Range (pg/ml) | Detectable (%) | Mean of Detectable (pg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | 30 | 1.82-3.57 | 100 | 2.94 |
Serum/Plasma – Thirty samples from apparently healthy rats were evaluated for the presence of TNF-α in this assay. No medical histories were available for the donors.
n.d. = non-detectable. Samples measured below the sensitivity are considered to be non-detectable.
Product Data Sheet
Background: TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha ), also known as cachectin and TNFSF1A, is the prototypic ligand of the TNF superfamily. It is a pleiotropic molecule that plays a central role in inflammation, immune system development, apoptosis, and lipid metabolism. TNF-alpha is also involved in a number of pathological conditions including asthma, Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, neuropathic pain, obesity, type 2 diabetes, septic shock, autoimmunity, and cancer.
Mouse TNF-alpha is synthesized as a 26 kDa type II transmembrane protein that consists of a 35 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 179 aa extracellular domain (ECD). Within the ECD, mouse TNF-alpha shares 95% aa identity with rat, and 80% aa identity with canine, equine, feline, human, rabbit, and porcine TNF-alpha. It is produced by a wide variety of immune, epithelial, endothelial, and tumor cells. TNF-alpha is assembled intracellularly to form a noncovalently linked homotrimer which is expressed on the cell surface.
Cell surface TNF-alpha can both induce the lysis of tumor cells and virus infected cells, and generate its own downstream cell signaling following ligation by soluble TNF RI. Shedding of membrane bound TNF-alpha by TACE/ADAM17 releases the bioactive cytokine, a 55 kDa soluble trimer containing the TNF-alpha extracellular domain.
TNF-alpha binds the ubiquitous 55-60 kDa TNF RI and the hematopoietic cell-restricted 78-80 kDa TNF RII, both of which are also expressed as homotrimers. Both type I and type II receptors bind TNF-alpha with comparable affinity and can promote NFkB activation. Only TNF RI, however, contains a cytoplasmic death domain which triggers the activation of apoptosis. Soluble forms of both types of receptors are released into human serum and urine, and can neutralize the biological activity of TNF.

