Mouse IL-1 alpha/IL-1 F1 enzyme-linked immunoassay kit
| Specification | 96 Test |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.05 pg/ml (10 μl) |
| Standard Curve Range | 1.37~1000 pg/ml |
| Standard Curve Gradient | 7 Points/3 Folds |
| Number of Incubations | 2 |
| Detectable sample | Liquid phase sample of soluble substances. For example: serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant, tissue grinding liquid, etc. |
| Sample Volume | 10 μl |
| Type | Fully Ready-to-Use |
| Operation Duration | 120min |
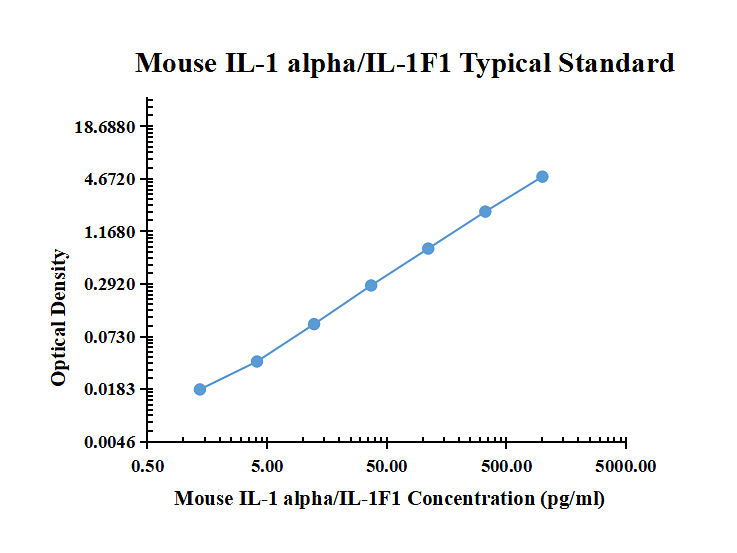
| pg/ml | O.D. | Average | Corrected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.0080 | 0.0069 | 0.0075 | |
| 1.37 | 0.0276 | 0.0258 | 0.0267 | 0.0193 |
| 4.12 | 0.0674 | 0.0614 | 0.0644 | 0.0570 |
| 12.35 | 0.1841 | 0.1823 | 0.1832 | 0.1758 |
| 37.04 | 0.5320 | 0.5206 | 0.5263 | 0.5189 |
| 111.11 | 1.4580 | 1.4540 | 1.4560 | 1.4486 |
| 333.33 | 3.0850 | 2.9580 | 3.0215 | 3.0141 |
| 1000.00 | 4.2378 | 4.2092 | 4.2235 | 4.2161 |
Precision
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample Number | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
| 22 | 22 | 22 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Average(pg/ml) | 31.84 | 78.30 | 274.99 | 35.74 | 90.87 | 293.41 |
| Standard Deviation | 1.70 | 3.62 | 11.32 | 1.21 | 3.02 | 13.13 |
| Coefficient of Variation(%) | 5.4 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 4.5 |
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay) Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays) Three samples of known concentration were tested six times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Spike Recovery
The spike recovery was evaluated by spiking 3 levels of mouse IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 into health mouse serum sample. The un-spiked serum was used as blank in this experiment.
The recovery ranged from 88% to 105% with an overall mean recovery of 99%.
Sample Values
| Sample Matrix | Sample Evaluated | Range (pg/ml) | Detectable (%) | Mean of Detectable (pg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | 30 | 4.98-28.97 | 100 | 15.61 |
Serum/Plasma – Thirty samples from apparently healthy mice were evaluated for the presence of IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 in this assay. No medical histories were available for the donors.
Product Data Sheet
Background: IL-1 alpha/IL-1 F1
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) is a name that designates two proteins, IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, which are the products of distinct genes, but which show approximately 25% amino acid sequence identity and which recognize the same cell surface receptors. Although IL-1 production is generally considered to be a consequence of inflammation, recent evidence suggests that IL-1 is also temporarily upregulated during bone formation and the menstrual cycle and can be induced in response to nervous system stimulation. In response to classic stimuli produced by inflammatory agents, infections or microbial endotoxins, a dramatic increase in the production of IL-1 by macrophages and various other cells is seen. Cells in particular known to produce IL-1 include osteoblasts, monocytes, macrophages, keratinocytes, Kupffer cells, hepatocytes, thymic and salivary gland epithelium, Schwann cells, fibroblasts and glia (oligodendroglia, astrocytes and microglia).
IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta are both synthesized as 31 kDa precursors that are subsequently cleaved into proteins with molecular weights of approximately 17,000 Da. Neither precursor contains a typical hydrophobic signal peptide sequence and most of the precursor form of IL-1 alpha remains in the cytosol of cells, although there is evidence for a membrane-bound form of the precursor form of IL-1 alpha. The IL-1 alpha precursor reportedly shows full biological activity in the EL-4 assay. Among various species, the amino acid sequence of mature IL-1 alpha is conserved 60% to 70% and human IL-1 has been found to be biologically active on murine cell lines. Both forms of IL-1 bind to the same receptors, designated type I and type II. Evidence suggests that only the type I receptor is capable of signal transduction and that the type II receptor may function as a decoy, binding IL-1 and thus preventing binding of IL-1 to the type I receptor.

