Mouse M-CSF/CSF1 enzyme-linked immunoassay kit
| Specification | 96 Test |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.31 pg/ml (10 μl) |
| Standard Curve Range | 6.86~5000 pg/ml |
| Standard Curve Gradient | 7 Points/3 Folds |
| Number of Incubations | 2 |
| Detectable sample | Liquid phase sample of soluble substances. For example: serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant, tissue grinding liquid, etc. |
| Sample Volume | 10 μl |
| Type | Fully Ready-to-Use |
| Operation Duration | 120min |
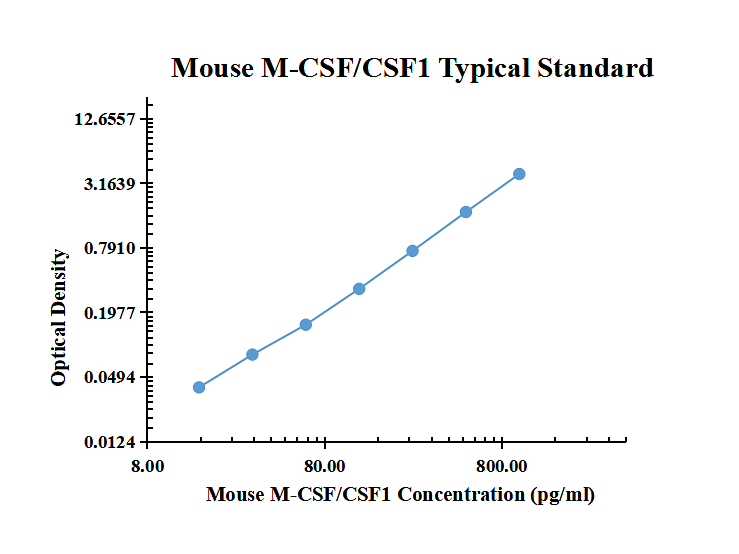
| pg/ml | O.D. | Average | Corrected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.0153 | 0.0169 | 0.0161 | |
| 6.86 | 0.0487 | 0.0427 | 0.0457 | 0.0296 |
| 20.58 | 0.1196 | 0.1191 | 0.1194 | 0.1033 |
| 61.73 | 0.3429 | 0.3280 | 0.3355 | 0.3194 |
| 185.19 | 0.9188 | 0.8179 | 0.8684 | 0.8523 |
| 555.56 | 2.1906 | 2.2550 | 2.2228 | 2.2067 |
| 1666.67 | 3.7043 | 3.3983 | 3.5513 | 3.5352 |
| 5000.00 | 4.1075 | 4.2155 | 4.1615 | 4.1454 |
Precision
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample Number | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
| 22 | 22 | 22 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Average(pg/ml) | 95.79 | 470.48 | 1171.32 | 97.6 | 458.2 | 1089.7 |
| Standard Deviation | 3.24 | 24.57 | 71.90 | 4.3 | 23.9 | 60.5 |
| Coefficient of Variation(%) | 3.4 | 5.2 | 6.1 | 4.4 | 5.2 | 5.6 |
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay) Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays) Three samples of known concentration were tested six times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Spike Recovery
The spike recovery was evaluated by spiking 3 levels of mouse M-CSF/CSF1 into health mouse serum sample. The un-spiked serum was used as blank in this experiment.
The recovery ranged from 83% to 115% with an overall mean recovery of 96%.
Sample Values
| Sample Matrix | Sample Evaluated | Range (pg/ml) | Detectable (%) | Mean of Detectable (pg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | 30 | 1419.67-3710.99 | 100 | 2145.38 |
Serum/Plasma – Thirty samples from apparently healthy mice were evaluated for the presence of M-CSF/CSF1 in this assay. No medical histories were available for the donors. n.d. = non-detectable. Samples measured below the sensitivity are considered to be non-detectable.
Product Data Sheet
Background: M-CSF/CSF1
M-CSF, also known as CSF-1, is a four-alpha-helical-bundle cytokine that is the primary regulator of macrophage survival, proliferation and differentiation. M-CSF is also essential for the survival and proliferation of osteoclast progenitors. M-CSF also primes and enhances macrophage killing of tumor cells and microorganisms, regulates the release of cytokines and other inflammatory modulators from macrophages, and stimulates pinocytosis. M-CSF increases during pregnancy to support implantation and growth of the decidua and placenta. Sources of M-CSF include fibroblasts, activated macrophages, endometrial secretory epithelium, bone marrow stromal cells and activated endothelial cells. The M-CSF receptor (c-fms) transduces its pleotropic effects and mediates its endocytosis. M-CSF mRNAs of various sizes occur. Full length human M-CSF transcripts encode a 522 amino acid (aa) type I transmembrane (TM) protein with a 464 aa extracellular region, a 21 aa TM domain, and a 37 aa cytoplasmic tail that forms a 140 kDa covalent dimer. Differential processing produces two proteolytically cleaved, secreted dimers. One is an N- and O- glycosylated 86 kDa dimer, while the other is modified by both glycosylation and chondroitin-sulfate proteoglycan (PG) to generate a 200 kDa subunit. Although PG-modified M-CSF can circulate, it may be immobilized by attachment to type V collagen. Shorter transcripts encode M-CSF that lack cleavage and PG sites and produce an N-glycosylated 68 kDa TM dimer and a slowly produced 44 kDa secreted dimer. Although forms may vary in activity and half-life, all contain the N-terminal 150 aa portion that is necessary and sufficient for interaction with the M-CSF receptor. The first 223 aa of mature human M-CSF shares 88%, 86%, 81% and 74% aa identity with corresponding regions of dog, cow, mouse and rat M-CSF, respectively. Human M-CSF is active in the mouse, but mouse M-CSF is reported to be species-specific.

