Mouse CCL5 / RANTES enzyme-linked immunoassay kit
| Specification | 96 Test |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 1.86 pg/ml (10 μl) |
| Standard Curve Range | 6.86~5000 pg/ml |
| Standard Curve Gradient | 7 Points/3 Folds |
| Number of Incubations | 2 |
| Detectable sample | Liquid phase sample of soluble substances. For example: serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant, tissue grinding liquid, etc. |
| Sample Volume | 10 μl |
| Type | Fully Ready-to-Use |
| Operation Duration | 120min |
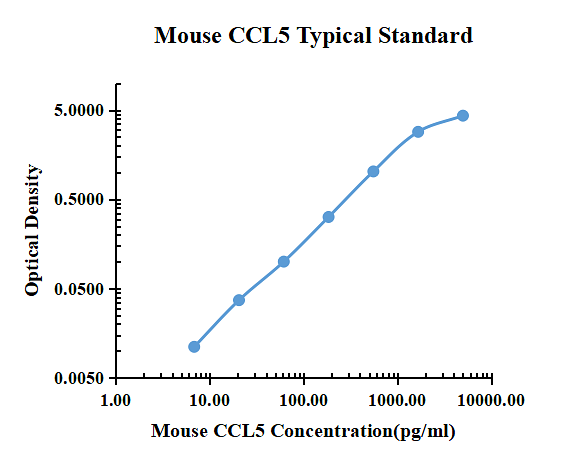
| pg/ml | O.D. | Average | Corrected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.0109 | 0.0120 | 0.0115 | |
| 6.86 | 0.0222 | 0.0229 | 0.0226 | 0.0111 |
| 20.58 | 0.0490 | 0.0479 | 0.0485 | 0.0370 |
| 61.73 | 0.1153 | 0.1077 | 0.1115 | 0.1001 |
| 185.19 | 0.3341 | 0.3222 | 0.3282 | 0.3167 |
| 555.56 | 1.0620 | 1.0130 | 1.0375 | 1.0261 |
| 1666.67 | 2.8860 | 2.8410 | 2.8635 | 2.8521 |
| 5000.00 | 4.3489 | 4.3304 | 4.3397 | 4.3282 |
Precision
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample Number | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
| 22 | 22 | 22 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Average(pg/ml) | 111.7 | 647.3 | 1815.5 | 107.4 | 516.0 | 1760.2 |
| Standard Deviation | 7.4 | 43.1 | 130.2 | 6.6 | 25.8 | 86.3 |
| Coefficient of Variation(%) | 6.6 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 6.1 | 5.0 | 4.9 |
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay) Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays) Three samples of known concentration were tested six times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Spike Recovery
The spike recovery was evaluated by spiking 3 levels of mouse CCL5 into health mouse serum sample. The un-spiked serum was used as blank in this experiment.
The recovery ranged from 99% to 125% with an overall mean recovery of 116%.
Sample Values
| Sample Matrix | Sample Evaluated | Range (pg/ml) | Detectable (%) | Mean of Detectable (pg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | 30 | 15.09-64.56 | 100 | 37.12 |
Serum/Plasma – Thirty samples from apparently healthy mice were evaluated for the presence of CCL5 in this assay. No medical histories were available for the donors. n.d. = non-detectable. Samples measured below the sensitivity are considered to be non-detectable.
Product Data Sheet
Background: CCL5 / RANTES
RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed and presumably Secreted), also known as CCL5, is a member of the "CC" subfamily of chemokines. It plays a primary role in the inflammatory immune response via its ability to chemoattract leukocytes and modulate their function. The cDNA for RANTES was initially discovered by subtractive hybridization as a T cell specific sequence. Human RANTES cDNA encodes a highly basic 91 amino acid (aa) residue precursor polypeptide with a 23 aa hydrophobic signal peptide that is cleaved to generate the 68 aa mature protein. Human RANTES exhibits approximately 85% homology with mouse RANTES at the deduced aa level.
RANTES is a potent chemoattractant for a number of different cell types including unstimulated CD4+/CD45RO+ memory T cells and stimulated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells with naive and memory phenotypes, NK cells, basophils, eosinophils, dendritic cells, mast cells, monocytes, and microglia. In addition to its effects on migration, RANTES can activate a number of cell types including T cells, monocytes, neutrophils, NK cells, dendritic cells, and astrocytes. T cell activation generally requires relatively high RANTES concentrations (~ 1 μM) and is dependent upon aggregation of the molecule and association with cell surface glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Whether this activity occurs in vivo remains unclear although in mice, intraperitoneally injected RANTES mutants that are unable to aggregate and/or bind GAG, are not capable of attracting leukocytes when compared to wild-type controls. Other in vivo studies show that RANTES knockout mice exhibit deficient recruitment of leukocytes to sites of acute inflammation.
RANTES, is known to interact with four identified seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors: CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CCR5 (22-25). RANTES stimulation can initiate a variety of signaling cascades that are cell context dependent. For instance, in T-cells, RANTES can stimulate elevations of intracellular Ca2+, and activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), protein kinase A, PI3-kinase, Rho GTPase, and JAK/STAT signaling pathways. The cytomegalovirus protein US28 exhibits significant homology with CC chemokine receptors and is capable of binding RANTES. Membrane-spanning US28 can, depending on the context, signal in a constitutive manner, bind RANTES and initiate G-protein-mediated signaling cascades, or sequester RANTES and potentially alter inflammatory responses.
The RANTES receptor CCR5 is also the primary co-receptor for R5 (M-tropic) variants of HIV-1. It has been demonstrated that RANTES, as well as the other CCR5 ligands, macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta, can competitively inhibit CCR5/HIV-1 interaction and suppress viral infection in vitro. These effects apparently do not require fully intact signaling from the CCR5 receptor. Consequently, modified forms of RANTES and non-peptide compounds that block the interaction of HIV-1 with CCR5 show promise for future therapies. In contrast, several reports show that RANTES can enhance in vitro replication of X4 (T-tropic) variants of HIV-1 that use CXCR4 as a co-receptor rather than CCR5. This activity usually requires relatively high RANTES concentrations (~μM) and is dependent upon interaction with cell surface GAGs, oligomerization, and activation of tyrosine kinase and MAP kinase signaling cascades.

