Human FGF-19 enzyme-linked immunoassay kit
| Specification | 96 Test |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.48 pg/ml (50 μl);4.11 pg/ml (10 μl) |
| Standard Curve Range | 15.63~1000 pg/ml |
| Standard Curve Gradient | 7 Points |
| Number of Incubations | 2 |
| Detectable sample | Liquid phase sample of soluble substances. For example: serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant, tissue grinding liquid, etc. |
| Sample Volume | 50 μl/10 μl |
| Type | Fully Ready-to-Use |
| Operation Duration | 120min |
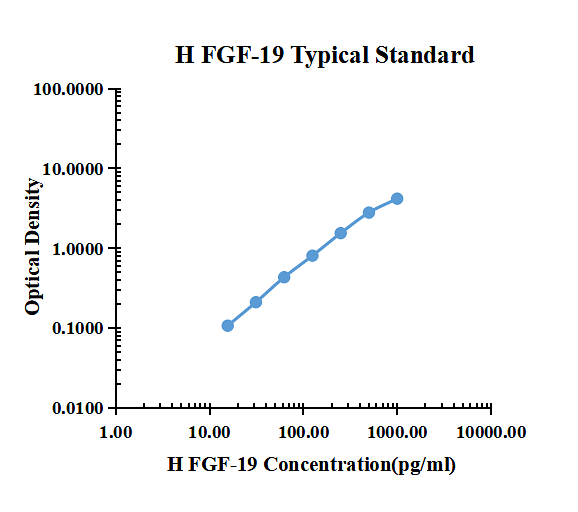
| pg/ml | O.D. | Average | Corrected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.0350 | 0.0324 | 0.0337 | |
| 15.63 | 0.1448 | 0.1364 | 0.1406 | 0.1069 |
| 31.25 | 0.2449 | 0.2436 | 0.2443 | 0.2106 |
| 62.50 | 0.4563 | 0.4771 | 0.4667 | 0.4330 |
| 125.00 | 0.8452 | 0.8358 | 0.8405 | 0.8068 |
| 250.00 | 1.6070 | 1.5490 | 1.5780 | 1.5443 |
| 500.00 | 2.8150 | 2.8420 | 2.8285 | 2.7948 |
| 1000.00 | 4.1933 | 4.2275 | 4.2104 | 4.1767 |
Precision
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample Number | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
| 22 | 22 | 22 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Average(pg/ml) | 22.6 | 111.5 | 323.0 | 22.1 | 109.5 | 329.4 |
| Standard Deviation | 1.4 | 4.5 | 11.3 | 0.5 | 2.6 | 12.7 |
| Coefficient of Variation(%) | 6.3 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 3.9 |
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay) Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays) Three samples of known concentration were tested six times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Spike Recovery
The spike recovery was evaluated by spiking 3 levels of human FGF-19 into health human serum sample. The un-spiked serum was used as blank in this experiment.
The recovery ranged from 86% to 107% with an overall mean recovery of 98%.
Sample Values
| Sample Matrix | Sample Evaluated | Range (pg/ml) | Detectable (%) | Mean of Detectable (pg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | 30 | 19.81-294.45 | 100 | 91.01 |
Serum/Plasma – Thirty samples from apparently healthy volunteers were evaluated for the presence of FGF-19 in this assay. No medical histories were available for the donors.
Product Data Sheet
Background: FGF-19
The Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family consists of at least 22 highly conserved proteins and are found in many species ranging from C. elegans and Drosophila to humans. FGFs are heparin-binding growth factors with a core 120 amino acid (aa) FGF domain that allows for a common tertiary structure. In general, FGFs are expressed during embryonic development and in restricted adult tissues. They act on cells of mesodermal and neuroectodermal origin to regulate diverse physiologic functions including angiogenesis, cell growth, pattern formation, metabolic regulation, cell migration, neurotrophic effects, and tissue repair. The activities of the FGF family are mediated by four receptors, FGF R1 through FGF R4. The receptors are transmembrane proteins with a tyrosine kinase domain and are thought to act as classical receptor tyrosine kinases. FGF R5/FGF RL1 has also been described, but lacks the kinase domain and signaling capability.
Human FGF-19 cDNA predicts a 251 aa precursor protein with a 22 aa signal peptide and a 229 aa secreted mature protein with no potential N-linked glycosylation sites. It shares approximately 50% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat FGF-15 and 62% aa sequence identity with chicken FGF-19. Unlike most FGFs, which bind to and activate more than one FGF receptor, FGF-19 appears to bind only FGF R4. Receptor binding is capable of activating MAP Kinase and inducing the Prolactin promoter. FGF-19 has two putative disulfide bonds, one of which is conserved in the FGF family. Uniquely, it also has an extended loop structure that may affect heparan sulfate binding.
The functional roles of FGF-19 continue to be elucidated and include developmental, metabolic, and tumorigenic activities. During chick embryogenesis, FGF-19 has been shown to act synergistically with Wnt-8c to initiate inner ear development. However, the mouse FGF-19 ortholog, FGF-15, is not required for this activity. FGF-19 is also expressed in the embryonic chicken eye where it may play a role in lens development. Questions regarding the functions of human FGF-19 have been addressed using ectopic expression. Transgenic over-expression of human FGF-19 in mice results in tumor formation, increased energy expenditure, decreased adiposity, and a resistance to weight gain in response to a high fat diet. Similar affects have been observed in mice treated intravenously with recombinant FGF-19.

